


The resulting structure becomes heterogeneous in nature.
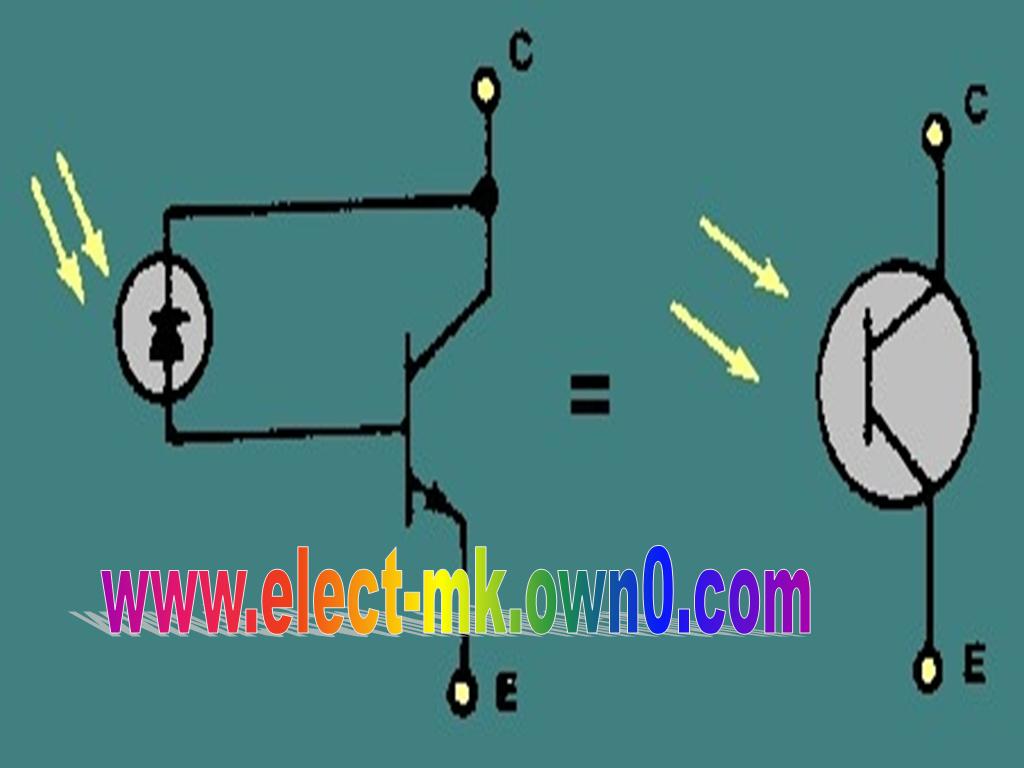
On the contrary, contemporarily, phototransistors are made up of Group-III and Group-V materials such as GaAs (Gallium Arsenide) in such a way that gallium and arsenide, each of these are used on either side of the transistor. The transistor which were used earlier was made of semiconductor material such as Germanium and Silicon and the resulting structure becomes a homogeneous material consist of either Silicon or Germanium. The collector and base region are formed by the techniques of ion-implantation and diffusion. This is because the more the light falls on the phototransistor the more current it will generate. The Phototransistors are manufactured in the similar way by which normal transistor is manufactured, the only difference is the area of the base and collector region in case of phototransistors is quite large as compared to the normal transistor. The circuit symbol of the phototransistor is described in the diagram below.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
